Conditions >>
A diabetic foot ulcer is one of the diabetic foot complications resulting in wounds under the foot and is the leading cause of lower limb amputation in Singapore. It is a type of wound that can occur on any area of the feet of individuals with diabetes. Diabetes can cause nerve damage and poor blood flow to the feet, leading to a loss of sensation and slower wound healing. Such damage makes individuals with diabetes particularly vulnerable to foot ulcers, which can become serious if not treated promptly and adequately.
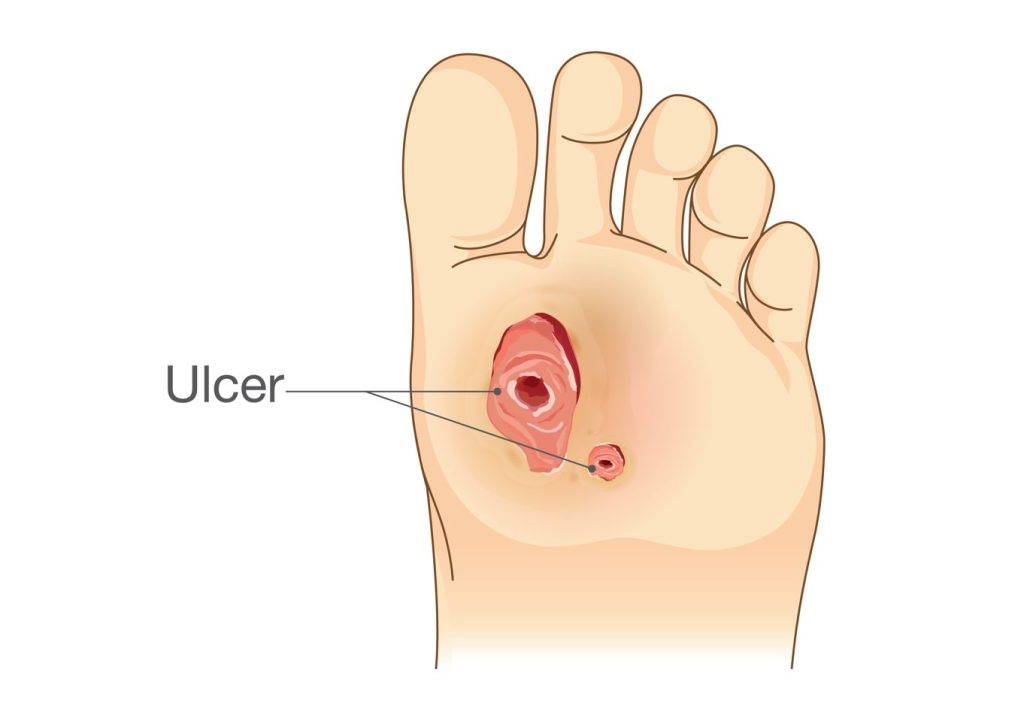
Diabetic foot ulcers and wounds result from several factors, including the following:
The symptoms of diabetic foot ulcers and wounds can range from mild to severe and may include:
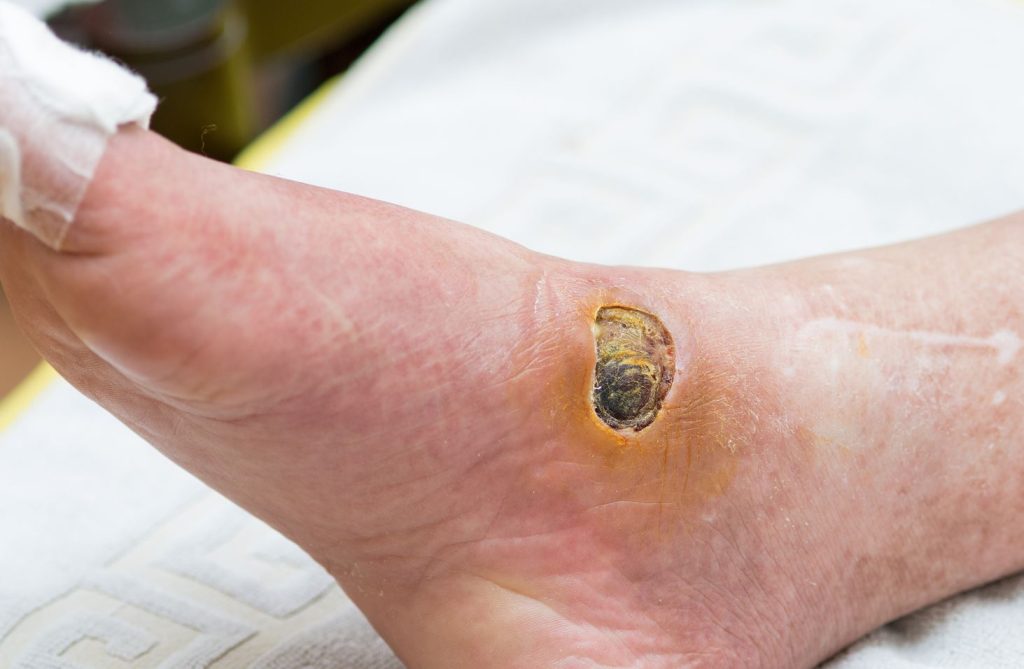
Proper management of diabetic foot ulcers and wounds must involve a comprehensive approach that addresses the underlying causes and promotes healing. Treatment options in Singapore typically include:
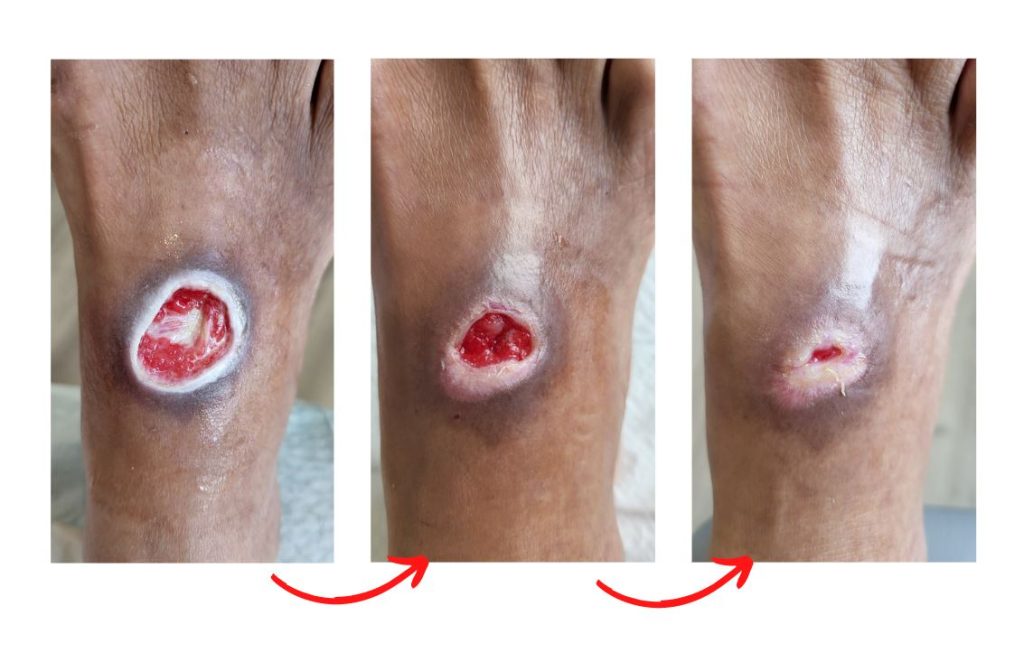
Preventing diabetic foot ulcers and wounds is crucial in managing this condition. Here are some tips to keep your feet healthy:
Diabetic foot complications can be debilitating, and it is essential to receive timely and evidence-based management. At Straits Podiatry, we specialize in diabetic foot care and offer various services to manage and prevent complications. We work with you to develop a personalized plan that addresses your unique needs and helps you achieve optimal foot health. Contact us today to schedule an appointment and take the first step towards healthy feet.
Related Articles:
Diabetic foot ulcers are a common complication among individuals with diabetes. In Singapore, around 11% of the adult population has diabetes, and approximately 25% of those with diabetes may develop a foot ulcer at some point. As a result, diabetic foot ulcers represent a significant public health concern in Singapore.
Diabetic foot ulcers typically result from a combination of factors related to diabetes, such as:
In Singapore, you can seek help for diabetic foot ulcers from a podiatrist or diabetes specialist at various healthcare facilities, including public hospitals, private clinics, and specialized diabetic foot clinics. Podiatrists work closely with endocrinologists, orthopaedic and vascular surgeons when treating diabetic foot complications.
To prevent diabetic foot ulcers in Singapore, you should:
The healing time for a diabetic foot ulcer varies depending on the severity of the ulcer, the individual’s overall health, and the management plan. Generally, it may take several weeks to months to heal. Severe cases with significant underlying health conditions may take more than a year.
However, severe ulcers or those complicated by infection may require extended recovery. Adhering to the management plan prescribed by your healthcare professional and maintaining proper foot care is crucial to promote healing and prevent complications.
You should consult your medical professional before seeking alternative medicine or traditional remedies. Some alternative therapies may interfere with conventional treatments, delay healing, or worsen the condition. Evidence-based medical therapies, such as wound care, debridement, and infection control, are essential for managing diabetic foot ulcers. Following your medical professional’s recommendations and being open about any alternative treatments you may be considering is vital.