Conditions >>
In-toe walking, also known as “Pigeon toes”, is a condition whereby a child is walking with their toes pointing inwards and facing each other. This condition is considered a form of gait abnormality and is one of the common causes of frequent tripping and falling in young children. It is also one of the most common paediatric conditions that parents often neglect even after noticing the problem.

It is estimated that 1 in 10 children between the age of 2 and 5 years has an in-toe walking condition, with up to 30% of children affected at the age of 4.
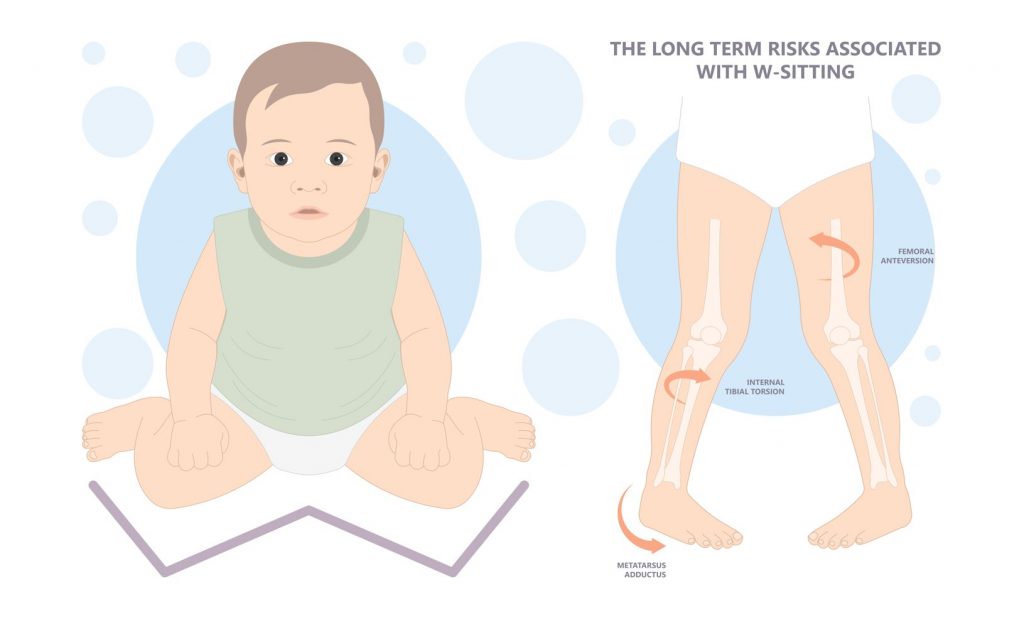
The most common cause of in-toe walking is atypical development of the musculoskeletal structure of the lower limb, which can occur at the hips, knee, leg, or foot level. There are also serious underlying conditions that can cause in-toe walking; therefore, a thorough assessment is necessary to evaluate the cause of the condition and determine if treatment is warranted.
The management for in-toeing walking depends largely on the underlying cause of the condition. Management, when required, should be initiated as early as possible so that there is a longer management=t window for change to occur. Children with mild cases of in-toe walking are possible to “grow out of it” by changing lifestyle habits, such as sitting cross-legged, along with proper stretching and strengthening exercises.