Conditions >>
Juvenile bunions, or juvenile hallux abductovalgus, are a type of foot deformity that affects the big toe joint of children or teenagers under the age of 18 years, where the big toe curves towards the lesser toes. The result of the deviation is a bony protrusion over the inner side of the big toe joint. The appearance of a juvenile bunion is similar to an adult bunion, with the only difference being the age of onset.
Juvenile bunions are considered a progressive deformity; therefore, it is expected that the big toe’s deviation worsens as a child grows up. Children affected by juvenile bunions will often not experience any discomfort in its early stages, however, as the deformity worsens, they will usually complain of pain and redness around the big toe joint.
Bunions have always been thought to be a hereditary condition. However, individuals affected by bunions were not born with this deformity but developed it as they grow. Therefore, what was inherited are the factors that cause bunions to develop over time.
Causes of juvenile bunions include:
Bunions can develop in either one foot or both feet, depending on whether the same risk factors are present in both feet. Children with underlying conditions such as scoliosis may have a leg length difference and cause bunions to develop on just one foot.
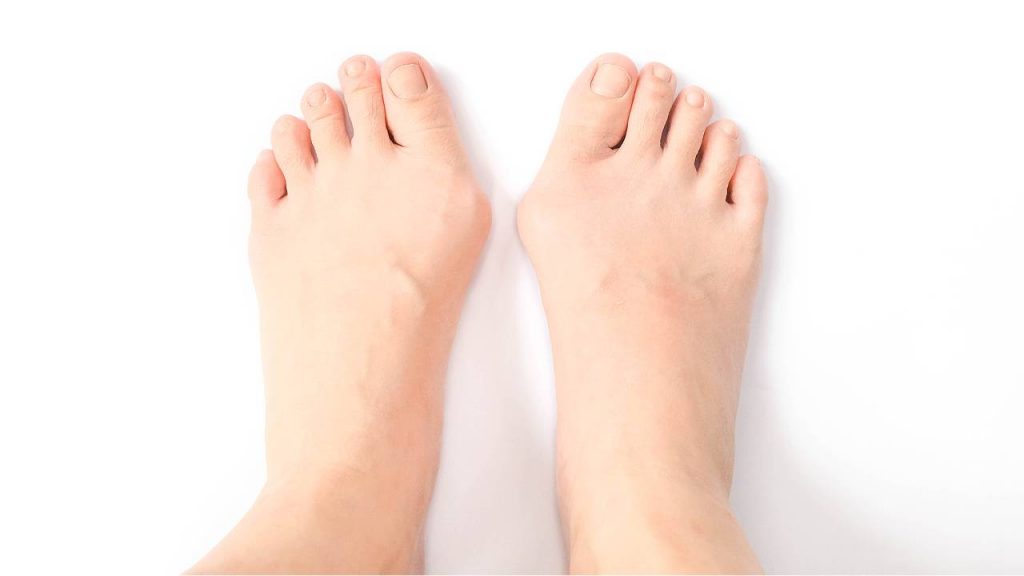
Children with juvenile bunions are often symptom-free during the early stages of the condition. The most noticeable sign of juvenile bunions is the “bony bump” developing on the inner side of the big toe joint. Symptoms often begin when the patient becomes more active or when the deformity progresses.
Signs and symptoms of juvenile bunions include:
Early detection and management are the keys to preventing juvenile bunions from worsening. Although the only solution to correct a bunion deformity is surgery, it is possible to prevent the big toe from deviating or “curving” further with non-surgical treatment. Besides, most painful bunions respond well to non-surgical options and do not often require surgery to relieve pain.
Treatment options for juvenile bunions in Singapore include: