Conditions >>
Knee osteoarthritis is a degenerative joint disease that causes knee pain, swelling, and stiffness. It is one of the most common knee conditions for the elderly, often explained as a “wear and tear” problem, and can severely impact their quality of life. Knee osteoarthritis occurs when there is a loss of articular cartilage within the knee, causing the joint space within the knee to narrow and eventually lead to bone-on-bone grinding during movement. As the condition progresses, bony spurs will develop and patients are often able to feel these painful bony lumps around the knee joint.
It’s important to note that not everyone who experiences osteoarthritis in their knees has experienced a traumatic injury or overuse of the joint. Some people simply have a genetic predisposition to developing knee osteoarthritis as they age.
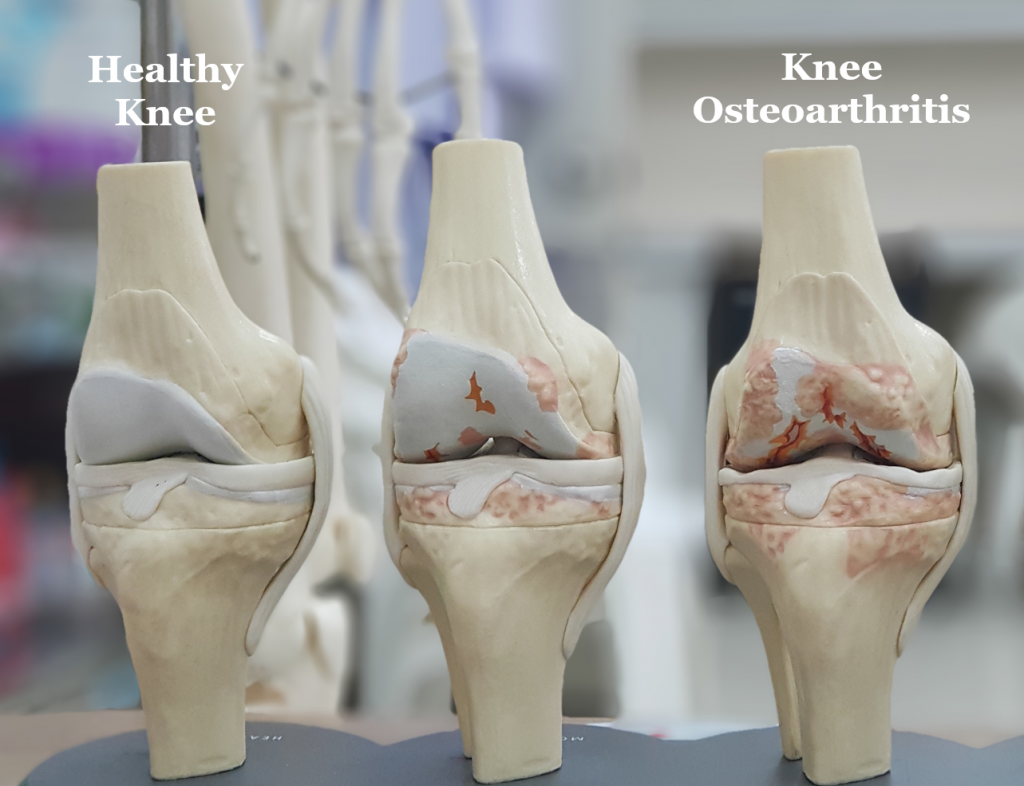
The knee joint is made up of two bones: the femur (thighbone) and the tibia (shinbone). There is also cartilage lining at each articulating end of the bone that allows for smooth movement. The knee joint has a small amount of fluid that lubricates the joints and helps keep them healthy. When the cartilage becomes worn out or damaged, the bones start to rub against one another and result in inflammation and pain.

There are 2 kinds of osteoarthritis, primary and secondary osteoarthritis. Primary osteoarthritis is the typical “wear and tear” of the joint due to age, whereas secondary osteoarthritis is caused by other factors.
Risk factors of osteoarthritis include the following:
Signs and symptoms of knee osteoarthritis include:
Most patients’ common misconception is that physical activity worsens their knee osteoarthritis. It is vital to maintain a healthy level of physical activity, especially one that has a low impact on the joints, to maintain mobility and function.
Management of knee osteoarthritis in Singapore includes: