Conditions >>
Knock knees, medically termed genu valgum, is a congenital structural abnormality that affects the angle of the knees. Parents often refer to knock knees as “X-shaped” legs, where the knees are touching one another whilst the feet are wide apart when standing.
Knock knees are determined by either the angular difference between the thigh bone (femur) and the leg bone (tibia) through an x-ray or by measuring the gap between the ankles when someone is standing with their knees together.
If within the normal reference range and age, knock knees are part of the normal development of a child. Children are expected to have mild knock knees after the age of 2 years, and peak at the age of 4 years.
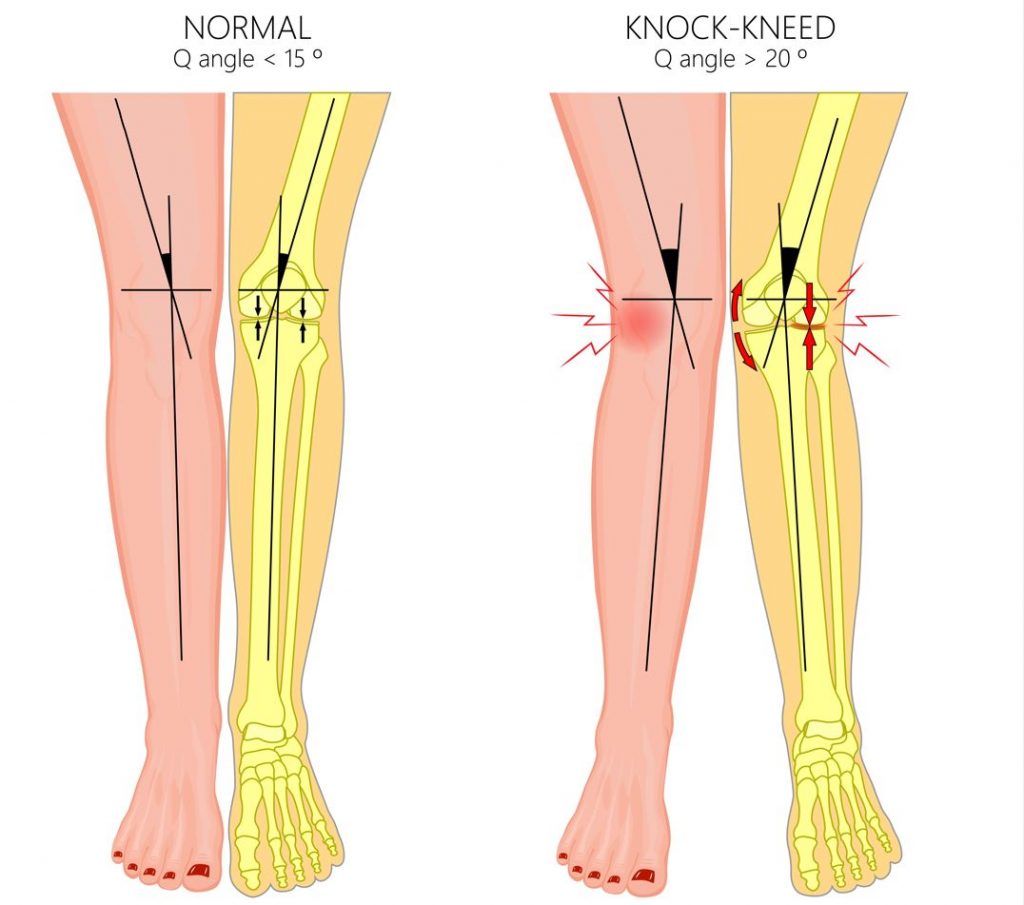
Knock knees are differentiated into physiological knock knees or pathological knock knees. Physiological knock knees are part of the normal development process of a child and are caused by the changes in the angles of the hip, thigh, knee, and foot. Physiological knock knees will generally resolve as the child age as the angles of the knock knees are mild. However, in moderate to severe cases, treatment will be necessary.
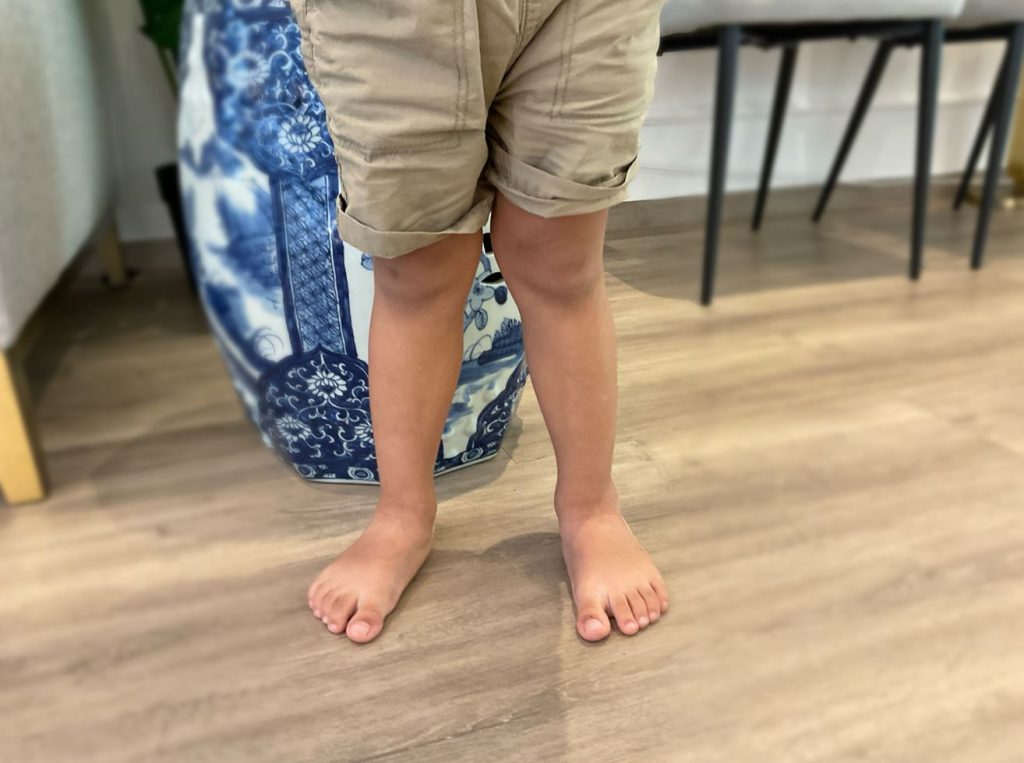
Children with knock knees may not present with any symptoms and are able to carry out normal activities without difficulty. However, knock knees can potentially lead to other knee problems as the child grows older.
Treatment for knock knees is dependent on the severity and the underlying cause of the problem. It usually involves the use of orthoses in conjunction with exercises to influence a change in the structural alignment.