Conditions >>
Leg length discrepancy, or leg length inequality, is a common condition that can cause foot pain, ankle pain, knee pain, hip pain, or back pain. This condition is characterized when one of the lower limbs is longer than the other. There are multiple factors that can cause leg length discrepancy, ranging from congenital (inborn), to injury-related, to iatrogenic (past medical treatment such as surgery). A leg length discrepancy of less than 1cm is often considered mild and some individuals may be asymptomatic. However, leg length discrepancy can cause tightness and stress on one side of the lower limb or body over time and is an associated risk factor for many musculoskeletal conditions of the lower limbs.
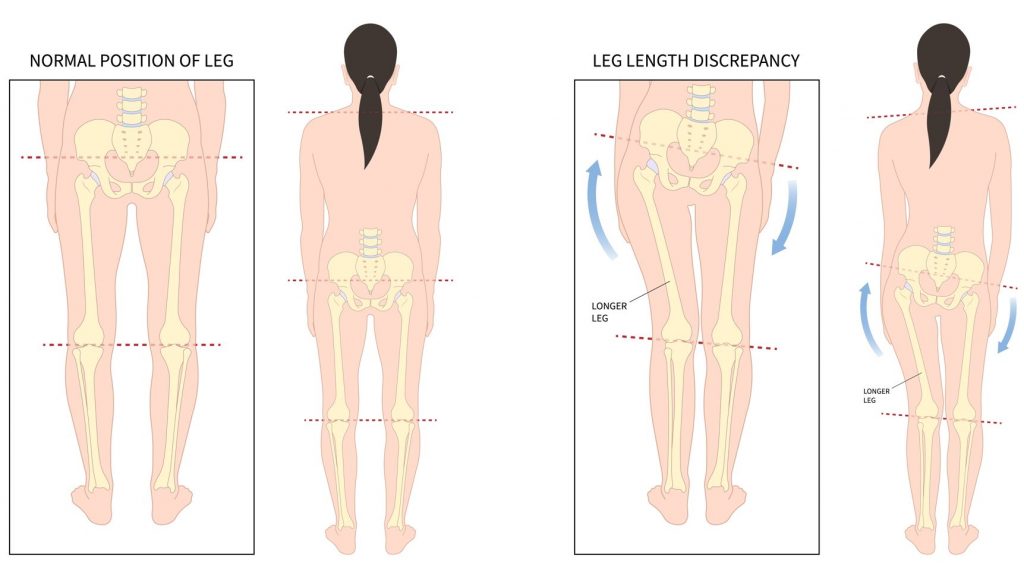
There are 2 types of leg length discrepancy: structural and functional.
Structural leg length discrepancy refers to an actual difference in the length of the bones of the femur, or tibia and fibula (thighbone or shinbones). This is typically not correctable or reducible through manipulation, adjustments, or bracing.
Functional leg length discrepancy refers to a difference in leg length when a person is standing or walking, but the actual length of the bones is equal. This is typically due to a structural malalignment of the body, such as scoliosis or muscular imbalances, resulting in a tilted hip position. This may be correctable or reducible if the underlying cause of structural malalignment is addressed appropriately.
This condition is most complex when there is a combination of structural and functional leg length discrepancy. Therefore it is crucial that your podiatrist determines the type through a thorough assessment.
Causes of leg length discrepancy include:
Most mild cases of leg length discrepancy are asymptomatic as the body is able to compensate for the difference, which are signs that are typically noticeable.
Signs of leg length discrepancy include:
Symptoms of leg length discrepancy include foot pain, ankle pain, knee pain, hip pain, and most commonly back pain. Most symptoms are related to the musculoskeletal condition that the leg length difference has caused.
Conditions that are associated with leg length discrepancy usually affect only one lower limb, and they include:
Management for leg length discrepancy usually involves using devices to help reduce the length differences. It is also essential that the individual undergo a stretching and strengthening program to reduce the compensation and adaptation he/she developed over time.
Treatment options for leg length discrepancy in Singapore include: