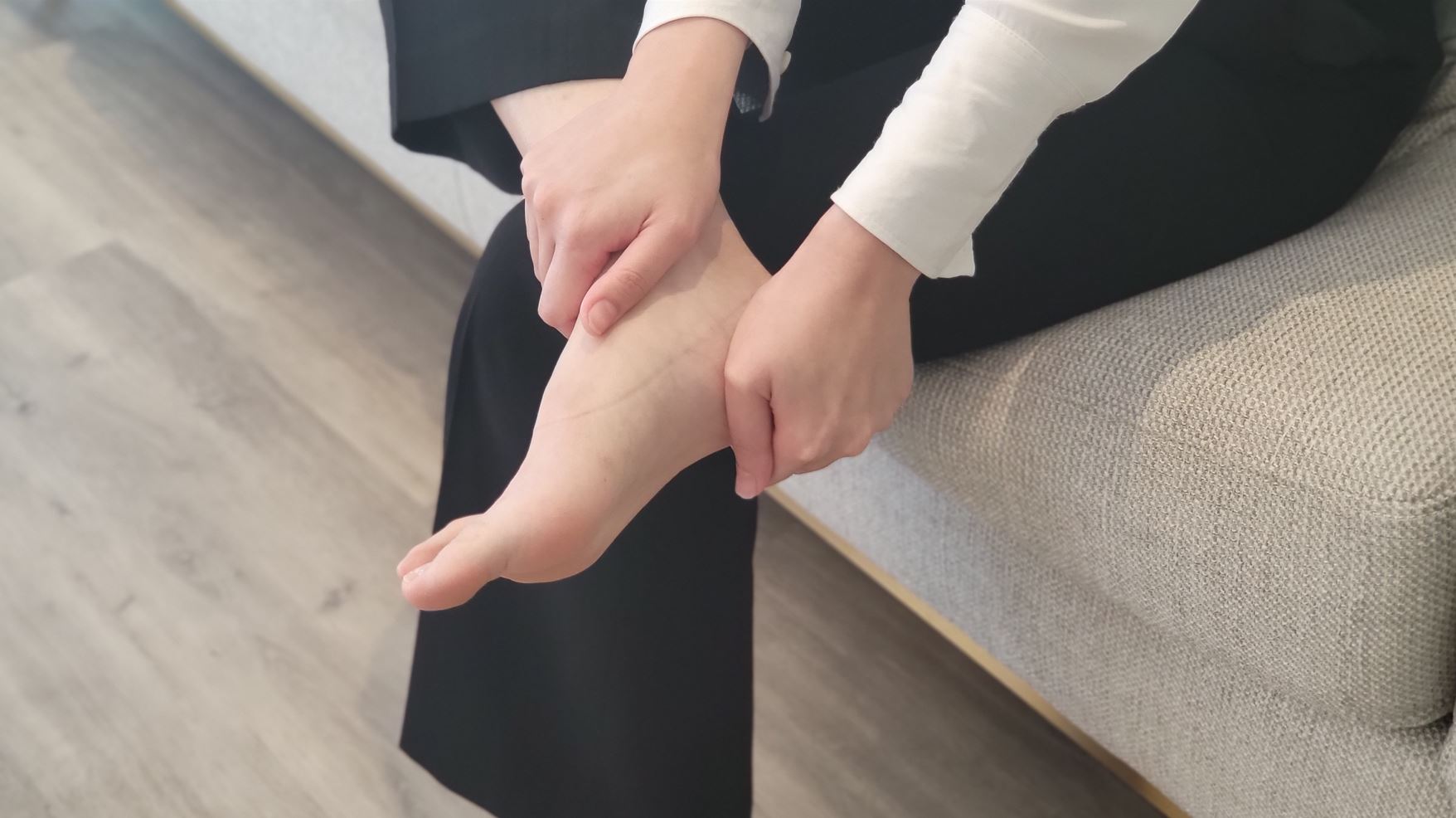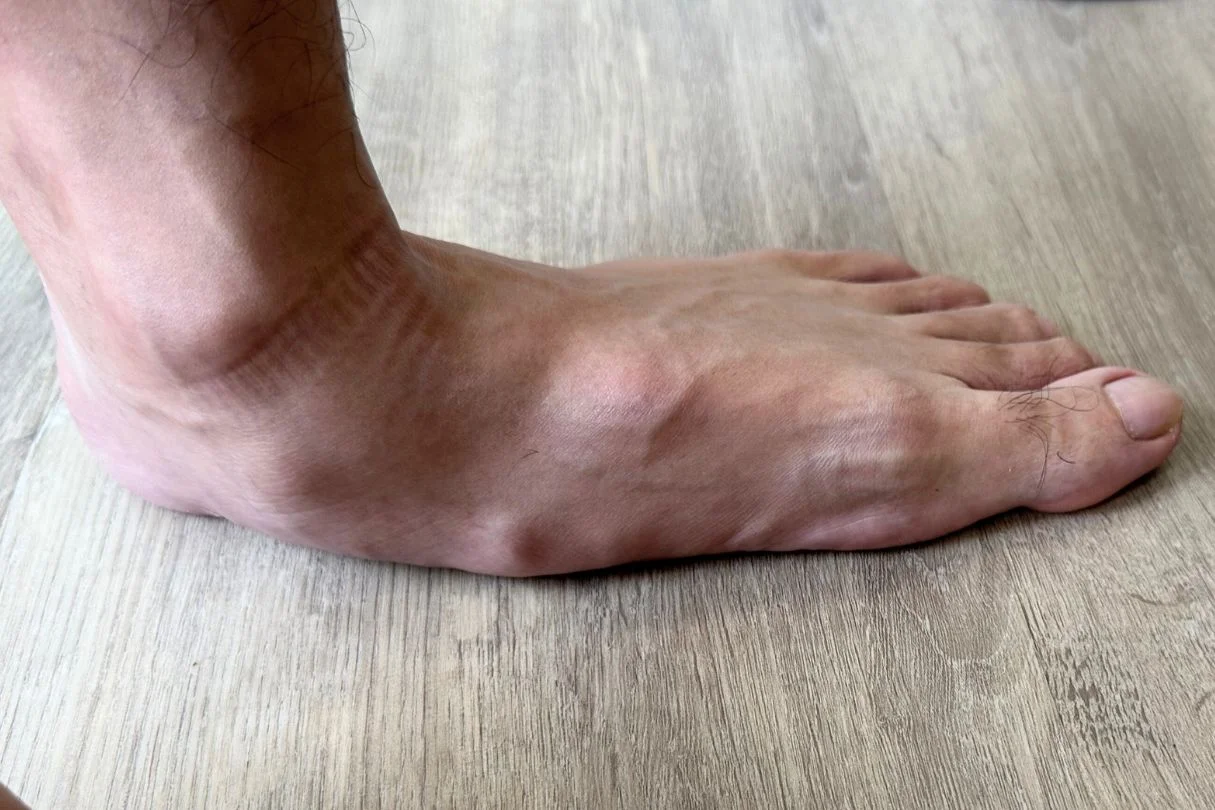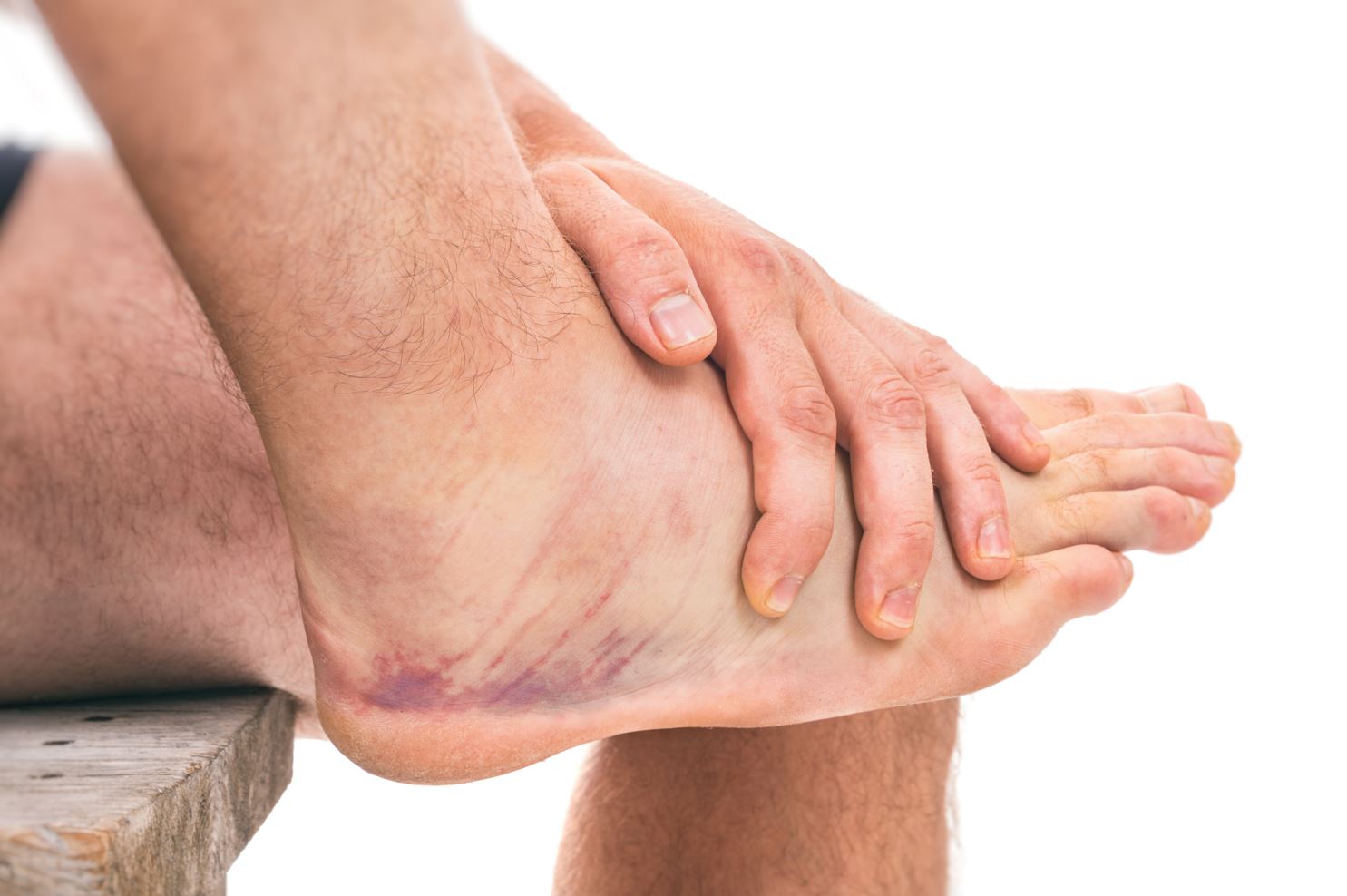
Acute Ankle Sprain
One of the most common injuries in the ankle is an acute ankle sprain. It occurs when the ankle is forcefully stretched beyond its normal range of motion. The patient’s ankle becomes swollen, and painful, and is difficult to put weight on that ankle. Ankle sprains often happen during sports such as basketball or badminton, and when running or hiking on uneven grounds.